Sometimes a species is so well studied it is hard to believe that there is anything new to discover about them. I’ve often felt this about badgers, the subject of my PhD research. Don’t get me wrong, I love badgers and they could never bore me. Ever. But there are just so many papers already written about every facet of their lives – their social structure, their ranging behaviour, their diet, their [really cool!] reproductive biology, and of course their role in the maintenance of bovine tuberculosis (TB), caused by Mycobacterium bovis infection. At this stage, what could we not know? But with advances in technology, come new discoveries!
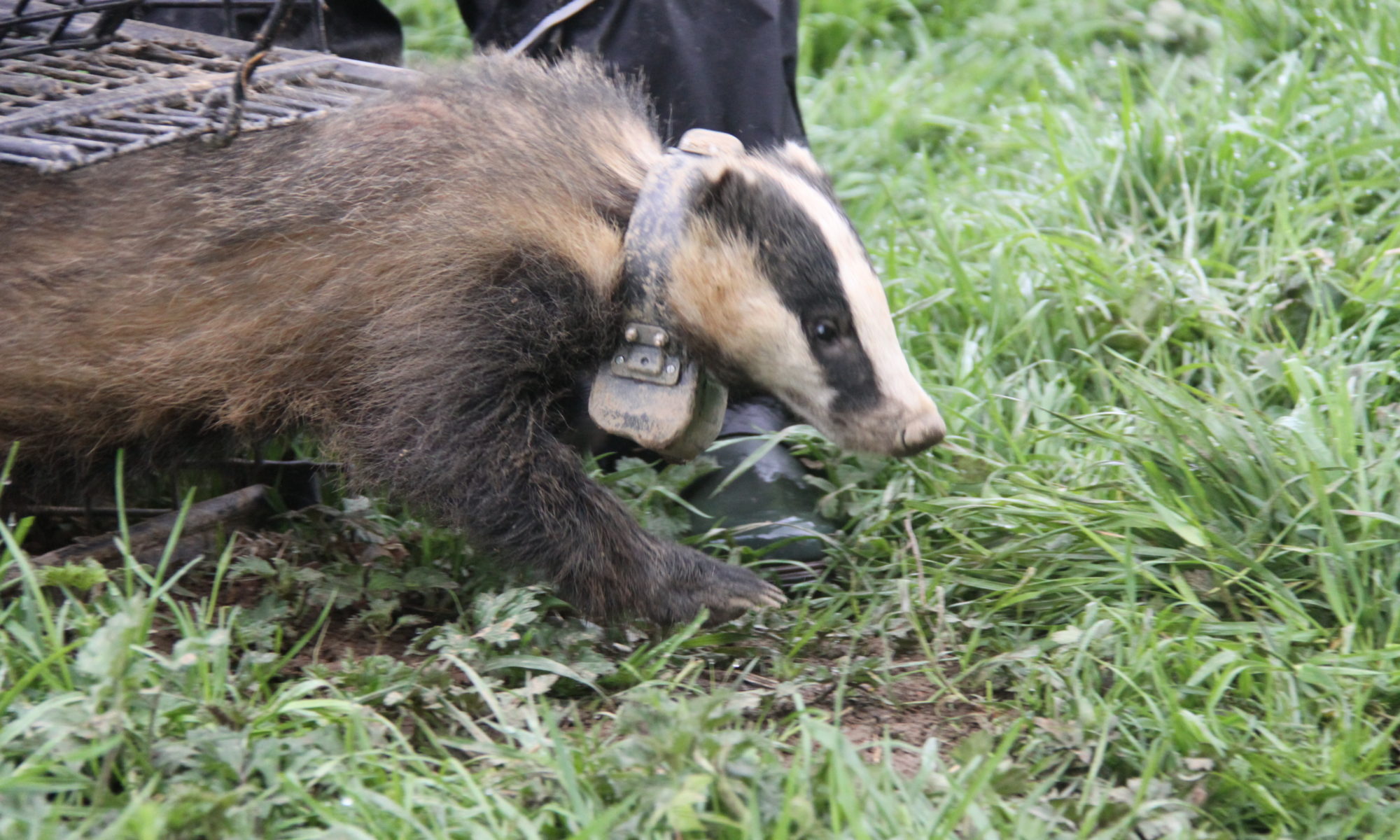
Our latest paper in the journal PLOS ONE describes a brand new “super-ranging” behaviour in badgers, which was revealed through the long-term deployment of GPS satellite tracking collars on a population of badgers in County Wicklow, Ireland by the Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine (DAFM) and the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS). Continue reading “Super-Ranging: Ranging behaviour in badgers isn’t always black and white!”